Anti Histamine ( anti Allergy) ; Definition, Types, Pharmacokinetic and Side effects
Antihistamines are a class of drugs that work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical that is released by the body during an allergic reaction. Antihistamines are most commonly used by people who have allergic reactions to pollen and other allergens. They are also used to treat a variety of other conditions such as stomach problems, colds, anxiety and more.
What are Allergy ?
Allergies are your body’s reaction to a foreign protein. Usually, these proteins (allergens) are harmless. However, if you have an allergy to a particular protein, your body’s defense system (immune system) overreacts to its presence in your body. In the case of an allergy, substances that are usually harmless and don’t bother some people, such as dust or animal dander, do bother you! Your body views these substances as “foreign,” which then triggers an overreaction by your body’s defense system that includes the release of histamine.
What is Histamine ?
Histamine is an organic compound which is involved in local immune responses and also acts as a neurotransmitter. It is also involved in the inflammatory response and is a mediator of pruritus. Histamine is produced by basophils and is found in tissues that are connected nearby. The permeability of white blood cells is increased by histamine and this allows the pathogens to get engaged with the infected tissues.
Commonest substances causing Allergies ?
- Food.
- Dust.
- Pollen.
- Pet dander, saliva or urine.
- Mold.
- Insect bites and stings.
- Latex.
- Certain medication/ Drugs.
- Congestion
- coughing.
- Wheezing, shortness of breath.
- nausea and vomiting.
- Itchy skin, hives and other skin rashes.
- A running or blocked nose, or sneezing.
- tiredness.
- Insomnia.
- Itchy, red, watering eyes.
- H-1 receptor antagonists or H-1 blockers
- H-2 receptor antagonists or H-2 blockers
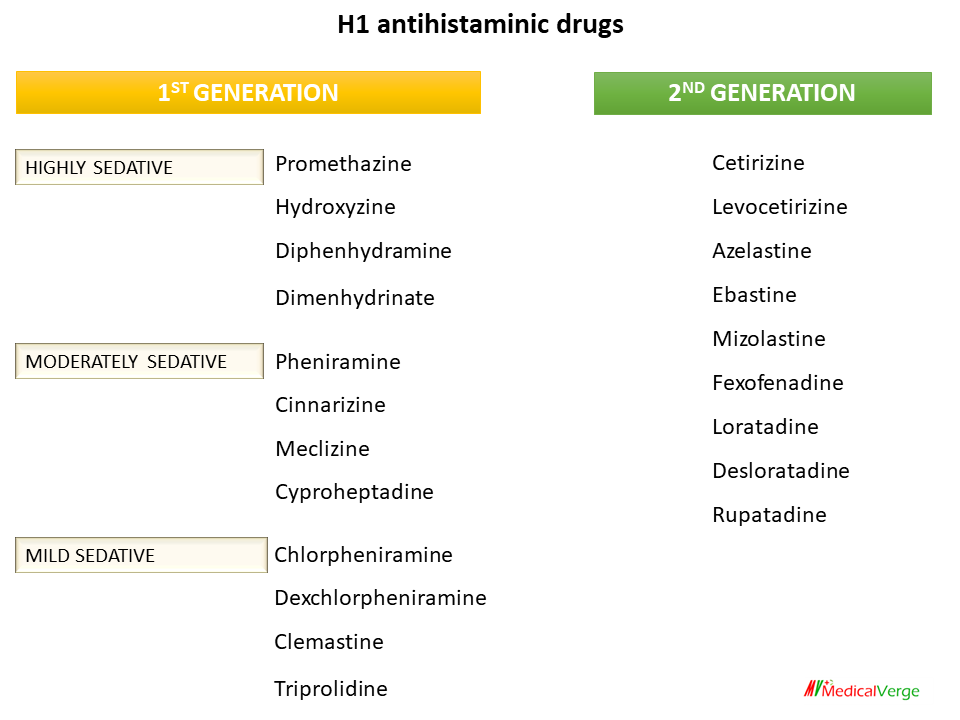
- First generation Antihistamines;
- H₁ antagonists, also called H₁ blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H₁ receptor, helping to relieve from allergic reaction.
- They work on histamine receptor in the brain and spinal cord along with other types of receptors.
- Second generation Antihistamines,
- Generally do not cause the sedation and drying seen in first-generation antihistamines
- Do not cross the blood-brain barrier as readily as First Generation compounds
- Lipophobicity
- Large molecular size
- Electrostatic charge
H-1 antihistamines treat:
- Allergic rhinitis/hay fever.
- Allergic conjunctivitis.
- Hives and other skin rashes.
- Colds.
- Food allergies.
- Hypersensitivity to certain drugs.
- Insect bites and stings.
First-generation H-1 antihistamines also treat:
- Insomnia.
- Motion sickness.
- Anxiety.
H-2 antihistamines treat:
- Heartburn.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Duodenal and gastric ulcers.
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Other conditions antihistamines treat include:
- Anorexia.
- Headaches.
- Anaphylaxis.
- Vertigo.
- Parkinson’s disease (to decrease stiffness and tremors).
- Some types of bone pain.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe antihistamines for even other conditions.
What are the Side Effects ;
First Generation ;
- Drowsiness.
- Dry mouth, dry eyes.
- Blurred or double vision.
- Dizziness and headache.
- Low blood pressure.
- Mucous thickening in the airways.
- Rapid heart rate.
- Difficulty urinating and constipation.
- Headache.
- Cough.
- Tiredness.
- Sore throat.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Drowsiness.
- Joint or muscle pain.
- Headache.
- Confusion in the elderly.
- Dizziness.
- Breast swelling and tenderness.
- Start with a low dose and increase it as needed.
- Take the antihistamine at least 30 minutes before exposure to the allergen.
- Avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how the antihistamine affects you.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the best antihistamine to take?
Antihistamines such as Claritin and Zyrtec are widely used over-the-counter. Doctors consider them to be safe and efficient allergy therapies. Both are antihistamines of the second generation. These antihistamines are less sedating than first-generation antihistamines.
Are antihistamines anti-inflammatory?
Antihistamines have lately been discovered to have anti-inflammatory effects that go beyond simple histamine receptor inhibition. New research, for example, reveals that these medications decrease the expression of cell adhesion molecules.
How quickly does antihistamine work?
Antihistamine medications usually start working within 30 minutes of taking them and are most effective within 1-2 hours of taking them. Antihistamines are more effective when taken on a regular basis as a preventative measure, rather than merely when symptoms appear.
What fruits are high in histamine?
Strawberries, bananas, pineapple, and pears are examples of citrus fruits. Eggplant, avocado, tomatoes, olives, and beans are examples of vegetables. Cheese, yoghurt, and processed cheese are examples of dairy products.
Does drinking water reduce histamine?
More than 95 percent of excess histamines are removed from the body through the urine, therefore water does help with histamine clearance. Drinking enough water keeps histamine levels safe and healthy, allowing your body to digest them efficiently.






Comments
Post a Comment