Exploring the Role of Gut Microbiota in Overall Health:
Definition,
Gut microbiota is the collection of microorganisms that live in the human gut. It is made up of trillions of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. The gut microbiota plays an important role in overall health including:
- Digestion and absorption of nutrients
- Immune function
- Brain health
- Mental health
- Weight management
- Skin health
- Cancer prevention
Types of gut microbiota,
There are two main types of gut microbiota:
- Probiotics: These are beneficial bacteria that can improve health. They can be found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
- Prebiotics: These are non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. They can be found in foods such as onions, garlic, and bananas.
Let's take a closer look at the different types of gut microbiota that exist within us:
Bacteroidetes: These bacteria are associated with the breakdown of complex carbohydrates and the regulation of appetite.
Firmicutes: These microbes are involved in the extraction of energy from food and are linked to obesity when their balance is disrupted.
Actinobacteria: These bacteria contribute to the production of important compounds like vitamins and short-chain fatty acids.
Proteobacteria: This group includes pathogens and can cause health issues when their numbers are too high.
Verrucomicrobia : These bacteria play a role in regulating metabolism and immune function.
Causes of gut microbiota imbalance,
There are many factors that can cause an imbalance in gut microbiota, including:
- Antibiotic use
- Stress
- Poor diet
- Lack of exercise
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Moving on, various health conditions have been linked to an imbalance in gut microbiota. Here's how you can cope with some of these conditions: Digestive Issues: Probiotics and fiber-rich foods can support gut health and alleviate digestive problems. Mental Health: There is growing evidence that gut microbiota plays a role in mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and autism spectrum disorder. Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation and yoga can help maintain a healthy gut-brain connection.
Autoimmune Disorders: Consult with a healthcare professional about specialized diets and medications to manage autoimmune conditions. Obesity: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, along with regular exercise, can aid in weight management.
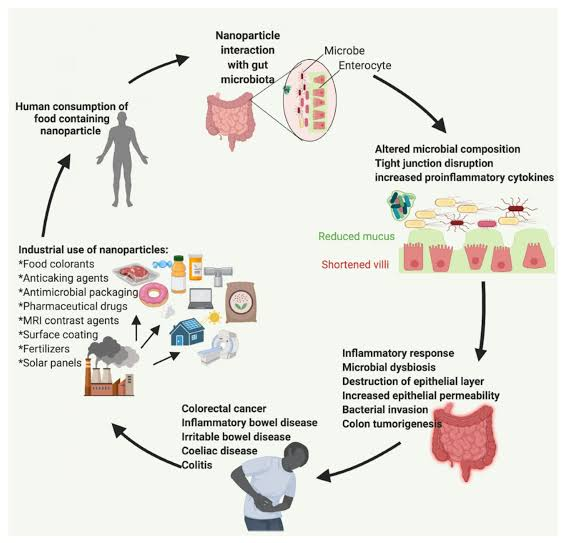
Cancer: Some studies have suggested that gut microbiota imbalance may be a risk factor for certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer.
Management of gut microbiota imbalance,
There are a number of things you can do to manage gut microbiota imbalance, including:
- Eat a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of red meat.
- Take probiotics and prebiotics.
- Manage stress.
- Get regular exercise.
- Get enough sleep.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- while cleanliness is important, excessive use of anti bacterial products can disrupt the natural balance of gut microbiota.
- Always consult your health care provider before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle.
Precautions,
If you are considering taking probiotics or prebiotics, it is important to talk to your doctor first. Some probiotics and prebiotics can interact with medications or other health conditions.
It is also important to note that there is still much that we don't know about gut microbiota and its role in health. More research is needed to fully understand how gut microbiota can be used to prevent and treat various health conditions.
Understanding the intricate relationship between gut microbiota and overall health is a fascinating journey that can lead to better well-being and a happier, healthier you.






Comments
Post a Comment