Exploring the Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Gut Health Impacts Mental Wellbeing"
Introduction:
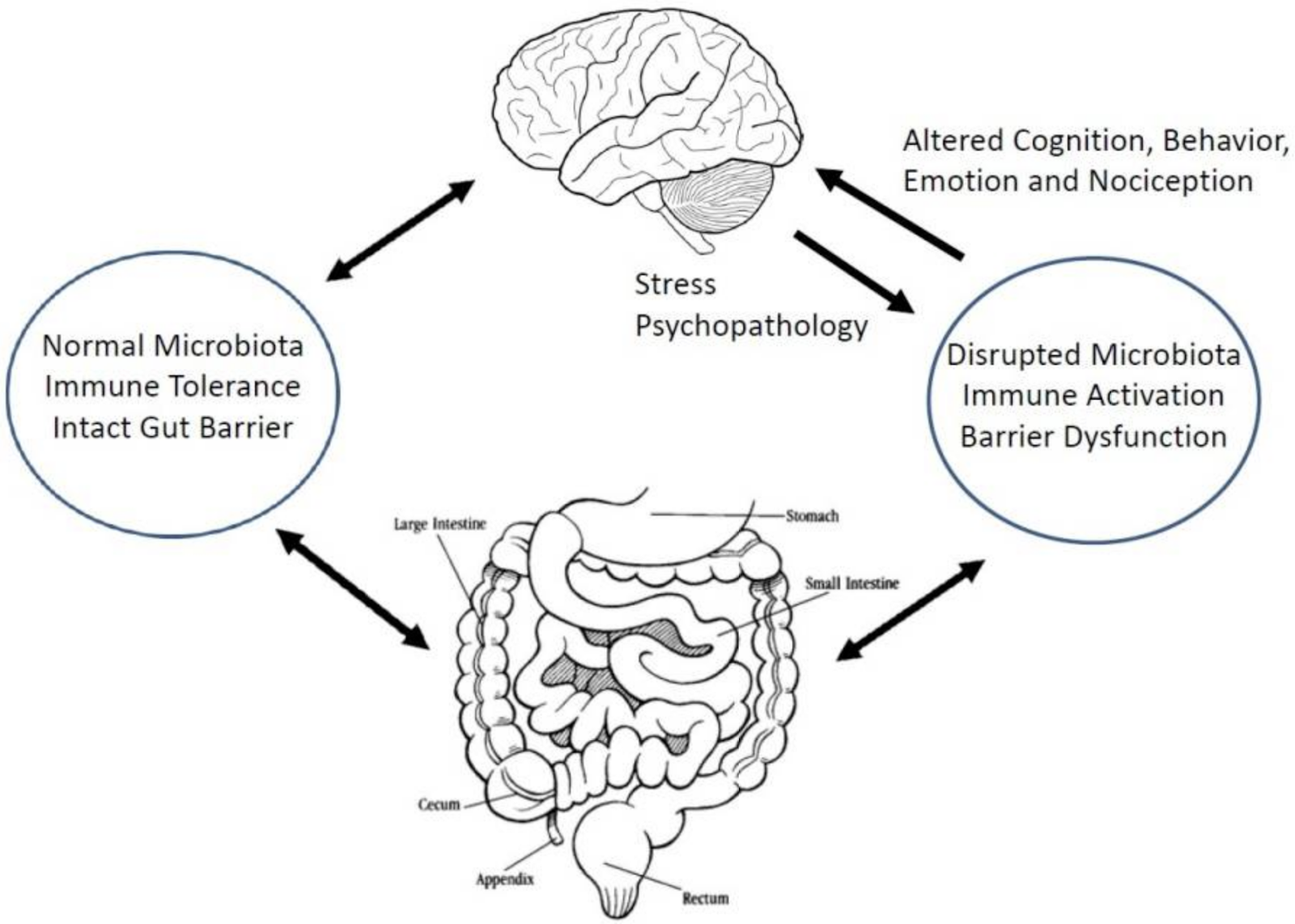
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication network that links the enteric and central nervous systems. This network is not only anatomical, but it extends to include endocrine, humoral, metabolic, and immune routes of communication as well. The autonomic nervous system, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and nerves within the gastrointestinal tract, all link the gut and the brain, allowing the brain to influence intestinal activities, including activity of functional immune effector cells; and the gut to influence mood, cognition, and mental health.
Emerging research has highlighted the intricate relationship between gut health and mental wellbeing, indicating that the state of our gut can significantly impact our emotions, mood, and cognitive functions. This article delves into the various aspects of the gut-brain connection, discussing the mechanisms, factors influencing it, and practical steps to promote better mental health through gut health.
The Gut - Brain Axis :
The gut-brain axis is the network of signals and communication pathways connecting the gut and the brain. The autonomic nervous system, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and nerves within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, all link the gut and the brain, allowing the brain to influence intestinal activities, including activity of functional immune effector cells; and the gut to influence mood, cognition, and mental health. The vagus nerve, a long cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in transmitting signals between the gut and brain. Additionally, the gut houses a complex ecosystem of microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota, which further influences this connection. Research suggests that gut health can impact mental health, and vice versa.
Mechanisms :
Neural Communication: The vagus nerve facilitates direct communication between the gut and brain. Signals travel in both directions, influencing processes such as digestion, mood regulation, and stress responses. Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: The gut microbiota produce various compounds, including neurotransmitters like serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which play pivotal roles in mood regulation. The gut microbiota also interact with the immune system, affecting systemic inflammation that can impact brain function.
Factors:
Diet: The foods we consume influence the composition and diversity of the gut microbiota. A diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the gut-brain axis, altering gut permeability and affecting the balance of gut bacteria. This can lead to inflammation and impact mental health. Antibiotics and Medications: Antibiotics, while useful, can disturb the gut microbiota's balance, potentially affecting mood and cognitive functions. Physical Activity: Regular exercise positively impacts gut health by promoting a diverse gut microbiota and reducing inflammation. Sleep: Poor sleep quality can disrupt gut microbiota and exacerbate stress-related effects on mental health.
Improving Mental Wellbeing with Gut Health :
Healthy diet: A healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to promote a healthy gut microbiota. Regular exercise: Exercise can help to improve gut motility and reduce inflammation, both of which can benefit gut health. Managing stress: Stress can have a negative impact on gut health. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature, can help to improve gut health. Sleep hygiene: Sleep is essential for gut health. When we don't get enough sleep, our gut microbiota can become imbalanced. Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria that are similar to the bacteria that naturally live in our gut. Taking probiotics can help to improve gut health and promote mental wellbeing.
If you are concerned about your gut health or mental wellbeing, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you to assess your risk factors and develop a personalized plan to improve your health.
Here are some additional tips for promoting mental wellbeing through gut health:
- Avoid processed foods: Processed foods are often high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and salt, which can all contribute to gut problems.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine: Alcohol and caffeine can irritate the gut lining and worsen gut problems.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can damage the gut lining and disrupt the gut microbiota.
- Regular medical checkups: Regular checkups can help to identify and treat any underlying health conditions that may be affecting your gut health or mental wellbeing.









Comments
Post a Comment